What is BIM and How Does It Work?
BIM (Building Information Modeling) is a digital framework that integrates architectural, engineering, and construction data to enhance project planning, design, and execution.
By creating a detailed 3D model, BIM enables collaboration, reduces errors, and improves efficiency throughout a building’s lifecycle. BIM is widely used in industries such as:
Architecture
For 3D visualization and design coordination
Construction
To improve project management and reduce errors
Engineering
For structural analysis and clash detection
Facility Management
To optimize building maintenance and operations
Want to implement BIM for your next project? Contact us for expert BIM services today.
Types of BIM Models
BIM technology encompasses various modeling approaches tailored to different project needs:
3D BIM: Visualization and Design
- Creates digital models with geometry, materials, and textures
- Used for design visualization and clash detection
- Enhances communication between architects and clients
4D BIM: Scheduling and Time Management
- Integrates time-related data into 3D models
- Helps in construction sequencing and project scheduling
- Reduces delays and improves efficiency
5D BIM: Cost Estimation
- Incorporates cost data, including materials and labor expenses
- Enhances budget forecasting and cost control
- Reduces financial risks through early-stage planning
6D BIM: Sustainability and Energy Analysis
- Evaluates energy consumption and environmental impact
- Helps optimize building performance and sustainability compliance
7D BIM: Facility Management and Maintenance
- Supports asset management and operational efficiency
- Provides digital documentation for long-term maintenance
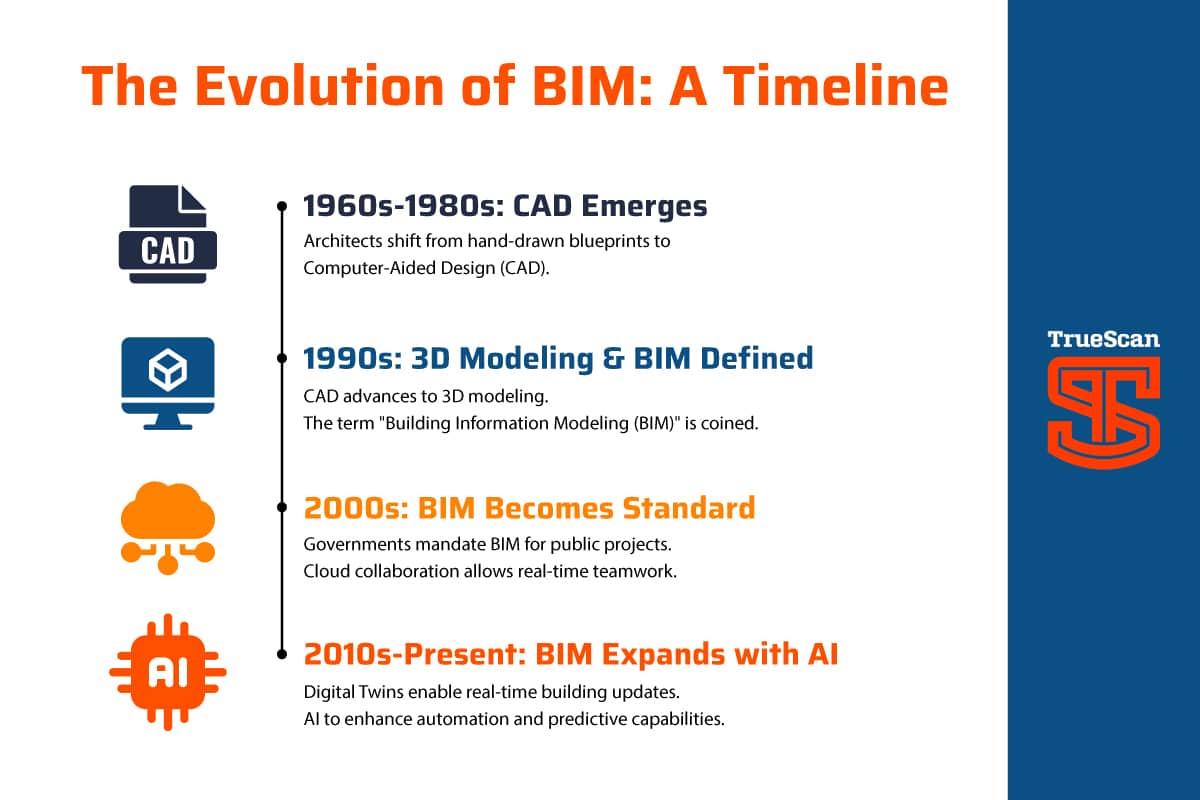
The History of BIM: From Paper to Digital Models
BIM’s journey spans several decades, evolving alongside advancements in computing and construction technology.
1960s-1980s: The Birth of CAD
- Before BIM, architects and engineers relied on hand-drawn blueprints.
- The introduction of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) in the 1960s allowed professionals to create digital drawings.
- In the 1970s, Charles Eastman, a professor at Carnegie Mellon University, pioneered early BIM concepts with research on “Building Description Systems.”
1990s: The Rise of 3D Modeling
- CAD systems advanced from 2D drawings to 3D modeling.
- The term “Building Information Modeling (BIM)” was coined in the early 1990s.
- Software companies like Autodesk and Graphisoft developed tools such as Revit and ArchiCAD, laying the foundation for modern BIM software.
2000s: BIM Becomes an Industry Standard
- Governments and large construction firms began adopting BIM for project planning.
- The UK, Scandinavia, and the U.S. introduced BIM guidelines and mandates for public infrastructure projects.
- Cloud-based collaboration tools emerged, allowing multiple teams to work on the same model simultaneously.
2010s-Present: The Expansion of BIM and Digital Twins
- BIM evolved into a full project lifecycle tool, integrating cost estimation (5D), sustainability analysis (6D), and facility management (7D).
- The construction industry embraced digital twins or virtual replicas of physical buildings that update in real time.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) further enhanced BIM’s predictive capabilities.
How Does BIM Work?
BIM software creates intelligent, data-rich 3D models that serve as a collaborative platform for all stakeholders in a construction project. The process includes:
Data Integration
BIM models combine geometric and non-geometric data, including materials, costs, and schedules, to provide a comprehensive project overview.
Collaborative Design
BIM allows architects, engineers, and contractors to work simultaneously on a centralized model, reducing design conflicts and improving efficiency.
Lifecycle Management
From initial design to demolition, BIM supports every stage of a building’s lifecycle, ensuring better decision-making and cost savings.
Applications of BIM in the Construction Industry
BIM in Design and Architecture
BIM software allows architects to visualize projects in 3D, making design changes easier and reducing miscommunication.
BIM in Construction and Project Management
Contractors use BIM models to streamline workflows, coordinate subcontractors, and enhance project scheduling.
BIM for Facility Management
After construction, BIM provides digital documentation that helps building owners manage operations, maintenance, and renovations efficiently.
BIM Services for Your Building Project
Looking for expert BIM services? Our team specializes in implementing BIM technology for construction, architecture, and facility management. Contact us today to learn more!